Spring Boot
Disadvantages of Microservices
- Microservices has all the associated complexities of the distributed system.
- There is a higher chance of failure during communication between different services.
- Difficult to manage a large number of services.
- The developer needs to solve the problem, such as network latency and load balancing.
- Complex testing over a distributed environment.
1. How does Spring Boot works?
Spring Boot automatically configures your application based on the dependencies you have added to the project by using annotation. The entry point of the spring boot application is the class that contains @SpringBootApplication annotation and the main method.
Spring Boot automatically scans all the components included in the project by using @ComponentScan annotation.
2. What does the @SpringBootApplication annotation do internally?
The @SpringBootApplication annotation is equivalent to using @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration, and @ComponentScan with their default attributes. Spring Boot enables the developer to use a single annotation instead of using multiple. But, as we know, Spring provided loosely coupled features that we can use for each annotation as per our project needs.
3. What is the purpose of using @ComponentScan in the class files?
Spring Boot application scans all the beans and package declarations when the application initializes. You need to add the @ComponentScan annotation for your class file to scan your components added to your project.
4. How does a spring boot application get started?
Just like any other Java program, a Spring Boot application must have a main method. This method serves as an entry point, which invokes the SpringApplication#run method to bootstrap the application.
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class);
// other statements
}
}5. What are starter dependencies?
Spring boot starter is a maven template that contains a collection of all the relevant transitive dependencies that are needed to start a particular functionality.
Like we need to import spring-boot-starter-web dependency for creating a web application.
<dependency>
<groupId> org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId> spring-boot-starter-web </artifactId>
</dependency>6. What is Spring Initializer?
Spring Initializer is a web application that helps you to create an initial spring boot project structure and provides a maven or gradle file to build your code. It solves the problem of setting up a framework when you are starting a project from scratch.
7. Features of Spring Boot that make it different?
- Creates stand-alone spring application with minimal configuration needed.
- It has embedded tomcat, jetty which makes it just code and run the application.
- Provide production-ready features such as metrics, health checks, and externalized configuration.
- Absolutely no requirement for XML configuration.
8. What are the advantages of using Spring Boot?
The advantages of Spring Boot are listed below:
- Easy to understand and develop spring applications.
- Spring Boot is nothing but an existing framework with the addition of an embedded HTTP server and annotation configuration which makes it easier to understand and faster the process of development.
- Increases productivity and reduces development time.
- Minimum configuration.
- We don’t need to write any XML configuration, only a few annotations are required to do the configuration.
9. What are the Spring Boot key components?
Below are the four key components of spring-boot:
- Spring Boot auto-configuration.
- Spring Boot CLI.
- Spring Boot starter POMs.
- Spring Boot Actuators.
10. How does Spring Boot works?
Spring Boot automatically configures your application based on the dependencies you have added to the project by using annotation. The entry point of the spring boot application is the class that contains @SpringBootApplication annotation and the main method.
Spring Boot automatically scans all the components included in the project by using @ComponentScan annotation.
11. What Are the Basic Annotations that Spring Boot Offers?
The primary annotations that Spring Boot offers reside in its org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure and its sub-packages. Here are a couple of basic ones:
@EnableAutoConfiguration – to make Spring Boot look for auto-configuration beans on its classpath and automatically apply them.
@SpringBootApplication – used to denote the main class of a Boot Application. This annotation combines @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration, and @ComponentScan annotations with their default attributes.
14. What is Spring Boot dependency management?
Spring Boot dependency management is used to manage dependencies and configuration automatically without you specifying the version for any of that dependencies.
15. Can we create a non-web application in Spring Boot?
Yes, we can create a non-web application by removing the web dependencies from the classpath along with changing the way Spring Boot creates the application context.
16. Is it possible to change the port of the embedded Tomcat server in Spring Boot?
Yes, it is possible. By using the server.port in the application.properties.
17. What is the default port of tomcat in spring boot?
The default port of the tomcat server-id 8080. It can be changed by adding sever.port properties in the application.property file.
18. Can we override or replace the Embedded tomcat server in Spring Boot?
Yes, we can replace the Embedded Tomcat server with any server by using the Starter dependency in the pom.xml file. Like you can use spring-boot-starter-jetty as a dependency for using a jetty server in your project.
19. Can we disable the default web server in the Spring boot application?
Yes, we can use application.properties to configure the web application type i.e spring.main.web-application-type=none.
20. How to disable a specific auto-configuration class?
You can use exclude attribute of @EnableAutoConfiguration if you want auto-configuration not to apply to any specific class.
//use of exclude
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude={className})21. Explain @RestController annotation in Sprint boot?
It is a combination of @Controller and @ResponseBody, used for creating a restful controller. It converts the response to JSON or XML. It ensures that data returned by each method will be written straight into the response body instead of returning a template.
22. What is the difference between @RestController and @Controller in Spring Boot?
@Controller Map of the model object to view or template and make it human readable but @RestController simply returns the object and object data is directly written in HTTP response as JSON or XML.
23. Describe the flow of HTTPS requests through the Spring Boot application?
On a high-level spring boot application follow the MVC pattern which is depicted in the below flow diagram.
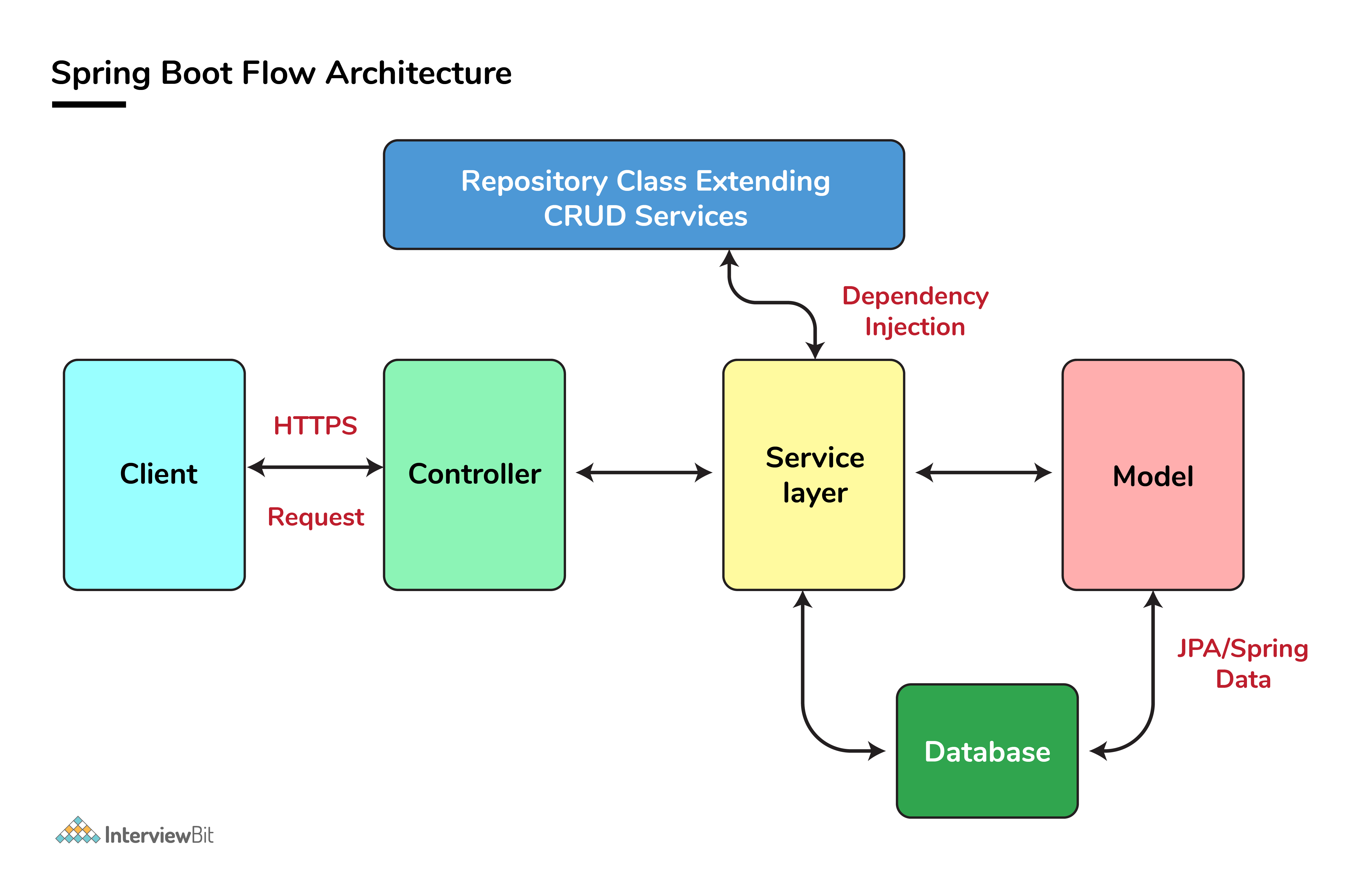
24. What is the difference between RequestMapping and GetMapping?
RequestMapping can be used with GET, POST, PUT, and many other request methods using the method attribute on the annotation. Whereas getMapping is only an extension of RequestMapping which helps you to improve on clarity on request.
25. What is the use of Profiles in spring boot?
While developing the application we deal with multiple environments such as dev, QA, Prod, and each environment requires a different configuration. For eg., we might be using an embedded H2 database for dev but for prod, we might have proprietary Oracle or DB2. Even if DBMS is the same across the environment, the URLs will be different.
To make this easy and clean, Spring has the provision of Profiles to keep the separate configuration of environments.
26. What is Spring Actuator? What are its advantages?
An actuator is an additional feature of Spring that helps you to monitor and manage your application when you push it to production. These actuators include auditing, health, CPU usage, HTTP hits, and metric gathering, and many more that are automatically applied to your application.
27. How to enable Actuator in Spring boot application?
To enable the spring actuator feature, we need to add the dependency of “spring-boot-starter-actuator” in pom.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId> org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId> spring-boot-starter-actuator </artifactId>
</dependency>28. What are the actuator-provided endpoints used for monitoring the Spring boot application?
Actuators provide below pre-defined endpoints to monitor our application -
- Health
- Info
- Beans
- Mappings
- Configprops
- Httptrace
- Heapdump
- Threaddump
- Shutdown
29. How to get the list of all the beans in your Spring boot application?
Spring Boot actuator “/Beans” is used to get the list of all the spring beans in your application.
30. How to check the environment properties in your Spring boot application?
Spring Boot actuator “/env” returns the list of all the environment properties of running the spring boot application.
31. How to enable debugging log in the spring boot application?
Debugging logs can be enabled in three ways -
- We can start the application with --debug switch.
- We can set the logging.level.root=debug property in application.property file.
- We can set the logging level of the root logger to debug in the supplied logging configuration file.
32. Where do we define properties in the Spring Boot application?
You can define both application and Spring boot-related properties into a file called application.properties. You can create this file manually or use Spring Initializer to create this file. You don’t need to do any special configuration to instruct Spring Boot to load this file, If it exists in classpath then spring boot automatically loads it and configure itself and the application code accordingly.
33. What is dependency Injection?
The process of injecting dependent bean objects into target bean objects is called dependency injection.
- Setter Injection: The IOC container will inject the dependent bean object into the target bean object by calling the setter method.
- Constructor Injection: The IOC container will inject the dependent bean object into the target bean object by calling the target bean constructor.
- Field Injection: The IOC container will inject the dependent bean object into the target bean object by Reflection API.
34. What is an IOC container?
IoC Container is a framework for implementing automatic dependency injection. It manages object creation and its life-time and also injects dependencies into the class.
35. @service annotation what is doing?
Well @Service annotation helps u specify that this class is a bean of service type and should be used to write buiseness logic of your application. Service class usuallly talk to the dao or data access layer to get data and combine them to required form that controller needs .
It is used to mark the class as a service provider. So overall @Service annotation is used with classes that provide some business functionalities. Spring context will autodetect these classes when annotation-based configuration and classpath scanning is used. Add the spring-context dependency in your pom.
@Service. We mark beans with @Service to indicate that they're holding the business logic. Besides being used in the service layer, there isn't any other special use for this annotation.
